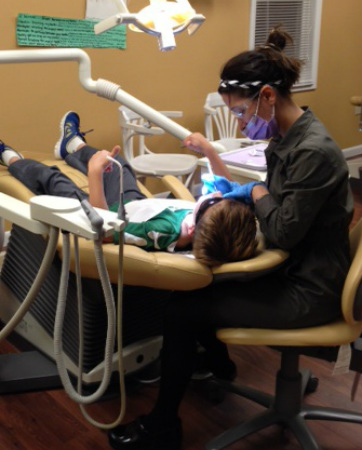
pediatric dentistry | services
what we doWe offer dental treatment to children ages 1-18 years old. Our services include:
|
"We are so lucky to have Dr. Sara in our community! She puts all kids at ease and she can handle any dental crisis! Thank you! - Patrick B's mom |
|
|
how we do itBecause oral health is a significant part of a child's overall health, it is very important to us that your child has a very positive dental experience. We are committed to providing the best dental care we can for your child. Out extensive training and education provide us with the skills necessary to work with children and their families:
|
FAQsWhat should I use to clean my baby's teeth?
A toothbrush will remove plaque bacteria that can lead to decay. Any soft-bristled toothbrush with a small head, preferably one designed specifically for infants, should be used at least once a day at bedtime. When should I take my child to the dentist for the first check-up? In order to prevent dental problems, your child should see a pediatric dentist when the first tooth appears, or no later than his/her first birthday. What is the difference between a pediatric dentist and a family dentist? Pediatric dentists are the pediatricians of dentistry. A pediatric dentist has two to three years specialty training following dental school and limits his/her practice to treating children only. Pediatric dentists are primary and specialty oral care providers for infants and children through adolescence, including those with special health needs. How do I find a pediatric dentist in my hometown? Click on the Find A Pediatric Dentist button located above. Enter your city, state and zip for a list of pediatric dentists nearest you. If your entries result in "no matching pediatric dentist records were found," broaden your search by entering the state only or nearest city and state. Are baby teeth really that important to my child? Primary, or "baby," teeth are important for many reasons. Not only do they help children speak clearly and chew naturally, they also aid in forming a path that permanent teeth can follow when they are ready to erupt. What should I do if my child has a toothache? First, rinse the irritated area with warm salt water and place a cold compress on the face if it is swollen. Give the child acetaminophen for any pain, rather than placing aspirin on the teeth or gums. Finally, see a dentist as soon as possible. Are thumbsucking and pacifier habits harmful for a child's teeth? Thumb and pacifier sucking habits will generally only become a problem if they go on for a very long period of time. Most children stop these habits on their own, but if they are still sucking their thumbs or fingers past the age of three, a mouth appliance may be recommended by your pediatric dentist. How can I prevent decay caused by nursing? Avoid nursing children to sleep or putting anything other than water in their bed-time bottle. Also, learn the proper way to brush and floss your child's teeth. Take your child to a pediatric dentist regularly to have his/her teeth and gums checked. The first dental visit should be scheduled by your child's first birthday. How often does my child need to see the pediatric dentist? A check-up every six months is recommended in order prevent cavities and other dental problems. However, your pediatric dentist can tell you when and how often your child should visit based on their personal oral health. Toothpaste: when should we begin using it and how much should we use? The sooner the better! Starting at birth, clean your child’s gums with a soft infant toothbrush or cloth and water. As soon as the teeth begin to appear, start brushing twice daily using fluoridated toothpaste and a soft, age-appropriate sized toothbrush. Use a "smear" of toothpaste to brush the teeth of a child less than 2 years of age. For the 2-5 year old, dispense a "pea-size" amount of toothpaste and perform or assist your child’s toothbrushing. Remember that young children do not have the ability to brush their teeth effectively.Children should spit out and not swallow excess toothpaste after brushing. |
|